Computer Security
This policy establishes the basic OS policy, that includes the necessary settings for User Rights Assignment, Security Options, Windows Firewall, Network List Manager, LAPS, Remote Assistance and Local Users and Groups (Preferences). This section will be broken down into individual sections so they can be explained further. As part of applying this GPO we are going to setup role based access to make changing administrative access easier in the future. Keep in mind, some organizations already have a well-designed Active Directory and will require the creation of new groups and OUs, but this document will attempt to provide some guidance if the organization does not already have something in place. It also helps to create new OUs and groups if you are migrating to a new design for tracking purposes. All security group and user account naming conventions are an example to help organizations that do not have a standard convention.
- In Active Directory create a new root level OU named Security Groups. This will contain all of the sub OUs for each of the different systems we are trying to segment. Now create an OU named Workstations under Security Groups. In this OU create the following Domain Local security groups.
- ACL_Workstation_LocalAdmins - This security group is an example naming convention.
- ACL_Workstation_RDPAccess - This security group is an example naming convention.
- ACL_Workstation_DenyLogonLocally - This security group is an example naming convention.
- In Active Directory create a new root level OU named Privileged Accounts. Inside this OU create the following sub OUs for each of sections that will have administrative accounts.
- Server Team
- Groups
- Users
- Help Desk
- Groups
- Users
- Server Team
- In the Groups OU create a new Domain Global Group named as below.
- USR_Desktop_WKAdmins ? This security group is an example naming convention.
- In the Users OU create a new user account based on company naming convention.
- Username.wk ? This username is an example naming convention.
- Add the username.wk account as a member of USR_Desktop_WKAdmins and then add USR_Desktop_WKAdmins as a member of ACL_Workstation_LocalAdmins.
User Rights Assignment¶
The first section will be Computer Configuration > Polices > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local policies > User Rights Assignment. This area of the Group Policy that controls much of the access to a system.
- Deny log on locally ? Adjust this setting to include the group below. First Remove the place holder name and add the domain group. This Group is to specifically designed to deny the ability to log on interactively. I use this for my vulnerability scanning account. It needs administrative access to the system but does not need to log on.
- ACL_Workstation_DenyLogonLocally.

- ACL_Workstation_DenyLogonLocally.
- Manage auditing and security log ? Adjust this setting to include the group below. First Remove the place holder name and add the domain group. The STIG states this should be a separate domain group but in small organizations it is easier to use the same group that is given local administrative access.
- ACL_Workstation_LocalAdmins.

- ACL_Workstation_LocalAdmins.
Security Options¶
Computer Configuration > Polices > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options. There are no settings to adjust in this section but there are a few settings that need some explanation.
- Accounts: Administrator account status ? Disabled. This means a new local administrator account needs to be created for use as a rescue account. The reason for disabling the Built-in Administrator account it to prevent brute force attacks. By disabling the Built-in account and creating a new one allows the account to lock out if an attacker is trying to brute force the password.
- Interactive logon: Number of previous logons to cache (in case domain controller is not available) ? The STIG requires this to be set at 4 or less. This GPO sets it to 0 because there is no reason to logon if the network is not available.
- Network security: Configure encryption types allowed for Kerberos ? the STIG has only the highest values set but sometimes environments have older systems that require RC4_HMAC_MD5 and DES_CBC_MD5/CRC.
NOTE: LAPTOPS WILL REQUIRE A SEPARATE POLICY WITH AT LEAST 4 LOGONS CACHED
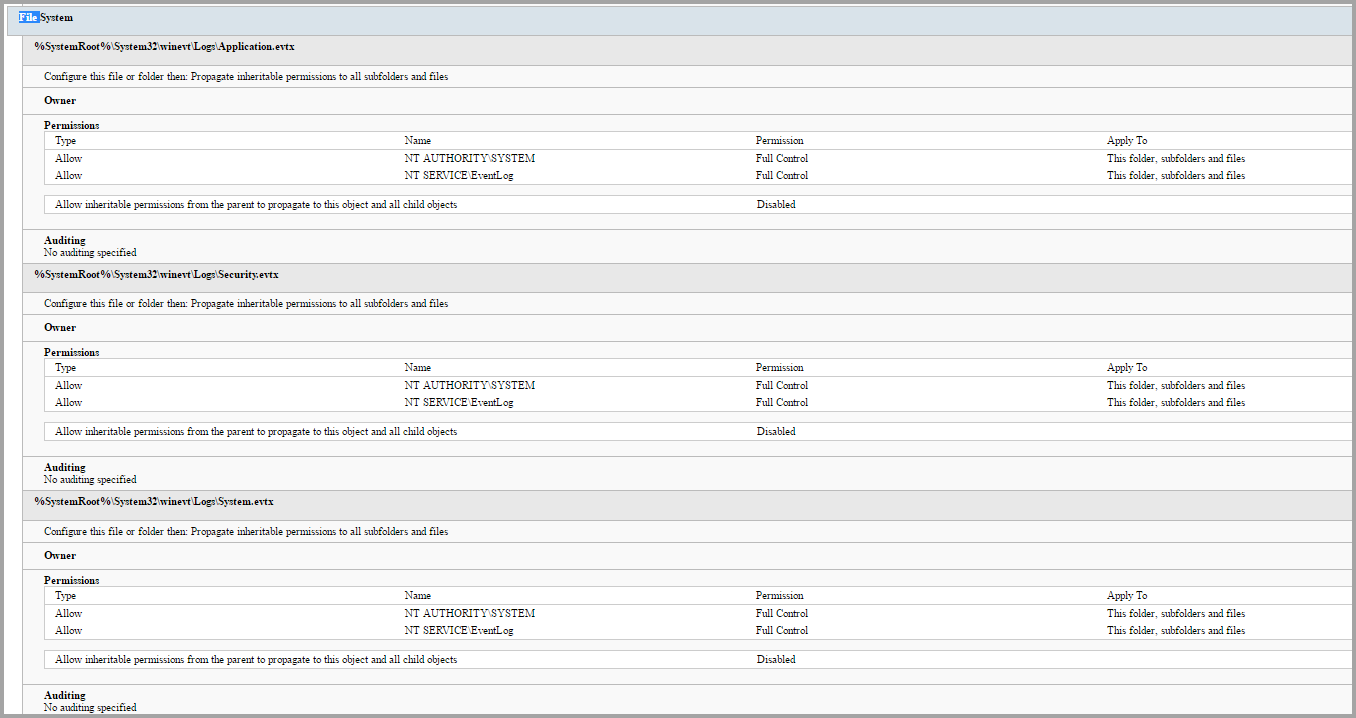
File System¶
- There are three entries for each of the event logs that need to be secured. Open each entry and add the domain group ACL_Workstation_LocalAdmins with full control.
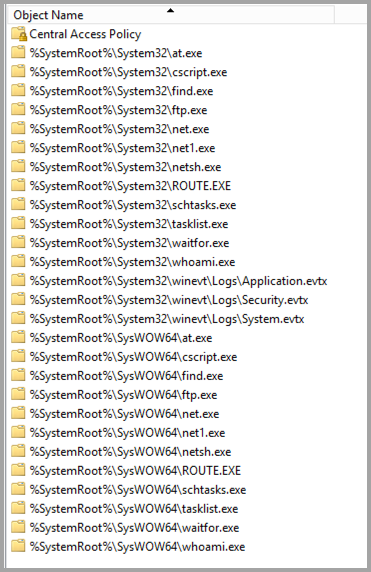
- Removing user permissions from administrative binaries. This is to help mitigate attackers recon use. This is not really a deterrent, but something to slow attackers down while in user space.
Windows Firewall¶
Computer Configuration > Polices > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security. Windows Firewall is an import element to reduce lateral movement of attackers. The firewall is set to block all inbound and allow all outbound traffic for all three profiles. The firewall will need to have some rules created/modified to fit your organization. The rules are setup to only use port/protocol and remote Address. It does not take advantage of the additional security measures that Microsoft allows for domain joined computers.
- The first rule is Allow admin/server access. Anyone who has administrative access to client systems should be restricted to a unique subnet so this rule can be restricted. It also mentions server access. Ideally there are only a few servers that initiate connections to client computers. An example would be a vulnerability scanner. Ensure any servers are added to this rule that need access to the clients.
- The second rule is to allow DHCP responses back. There is a specific setting to allow unicast responses back to the client but I have found that sometimes does not work, so a rule was created to specifically allow the DHCP responses back.
Windows AppLocker¶
Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Application Control Policies.
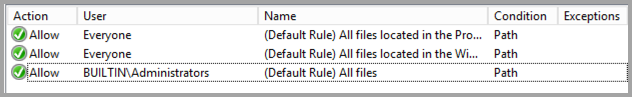
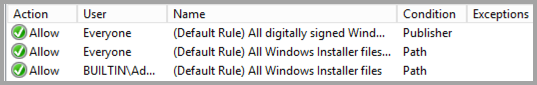
AppLocker is set to enforced with default policies. It also duplicates the restrictions for users executing binaries. Pick one of the options, i.e. File System permission restrictions or AppLocker and remove the other one.
-
Executable rules.
-
Windows Installer Rules.
-
Script Rules.
-
Packaged App Rules.
Network List Manager Policies¶
Computer Configuration > Polices > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Network List Manager Polices. These settings work in conjunction with the Windows Firewall and should be set. All unidentified and identifying networks have been forced to use public.
- Domainname.com Set the Name option to the organizations name.
Local Account Password Solution (LAPS)¶
LAPS is a Microsoft solution to manage the password of the local administrator account. This protects systems by setting a different randomized password on the clients. It then stores the password in the Active Directory computer object. Download the LAPS solution from Microsoft here. If LAPS is not configured the GPO will have no affect on the systems, except to generate errors in the event logs.
- LAPS can be download from here: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=46899
NOTE: IN ORDER TO CONFIGURE THE LAPS SETTINGS, IT IS ASSUMED THE SOLUTION HAS BEEN DEPLOYED ALREADY.
Name of administrator account to manage ? Modify this setting to the name of the Local Administrator account you created.
Offer Remote Assistance¶
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Remote Assistance Configure Offer Remote Assistance. Modify this setting and click on ?Show? and add in the ACL_Workstation_LocalAdmins group created earlier in this paper.
NOTE: IF YOUR COMPANY DOES NOT USE REMOTE ASSISTANCE, DISABLE THIS SETTING.
Preferences¶
Computer Configuration > Preferences > Control Panel Settings > Local Users and Groups. These are the settings to control access to the local groups on the client computers. Sort the accounts by the Order column. In each of the following Preferences remove my placeholders and add the appropriate local user or domain account.
-
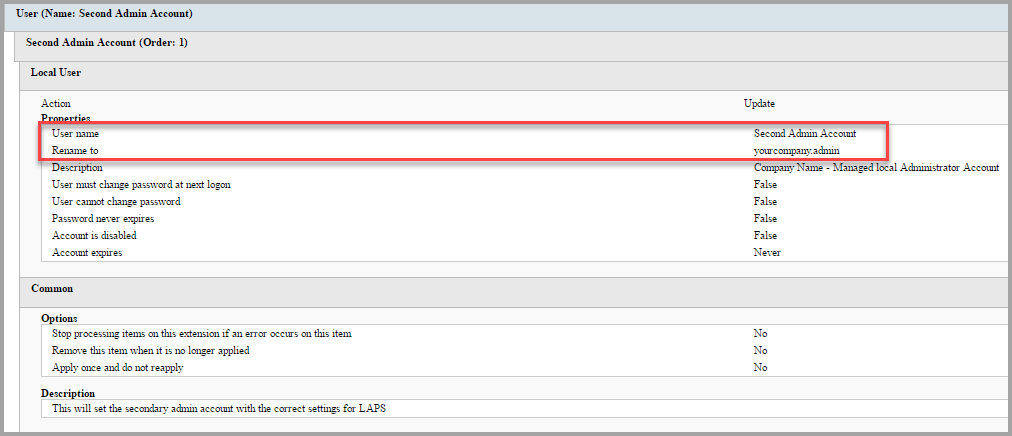
Second Admin Account ? If you do not already have a secondary local administrator account edit the place holder, type an account name in the ?User name? field and remove the text in the ?Rename to? field. This will create the account and set the appropriate options for the account.
-
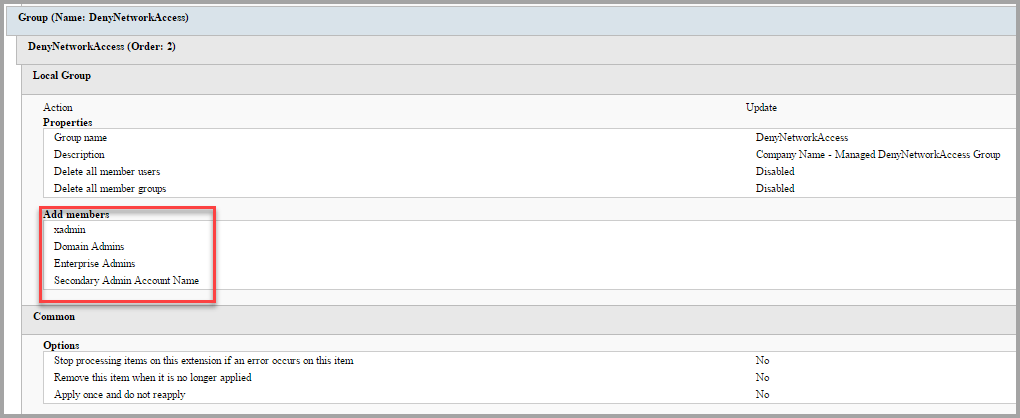
DenyNetworkAccess ? This group is designed to restrict network access to the client computer from privileged accounts. You can view its use in the User Rights section. Modify this setting and change the place holder account with the name of the secondary admin account.
-
Administrators (built-in) ? This group is designed to manage the local administrators group. Modify this setting and remove the placeholders and add your secondary admin account and the domain group ACL_Workstation_LocalAdmins. This Preference will add your newly created secondary admin account to the Administrators group.
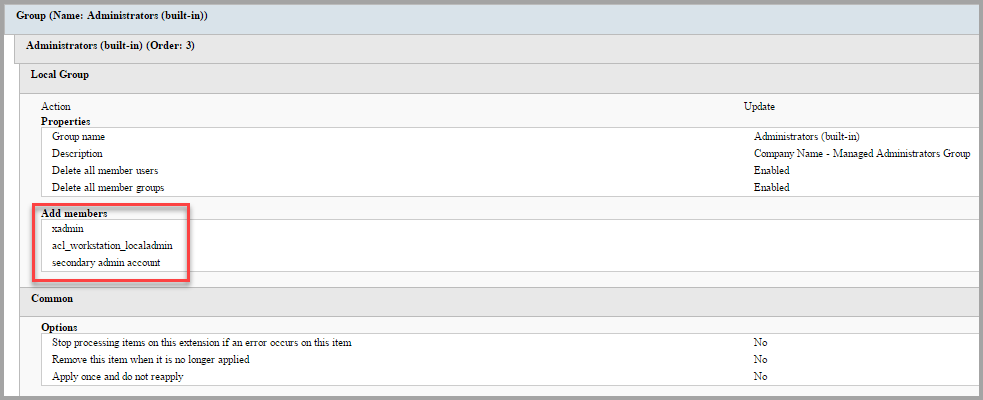
-
Remote Desktop Users (built-in) ? This group is designed to manage the accounts that can RDP the client computers. Modify this setting and add the Domain Local group that was created earlier. ACL_Workstation_RDPAccess.
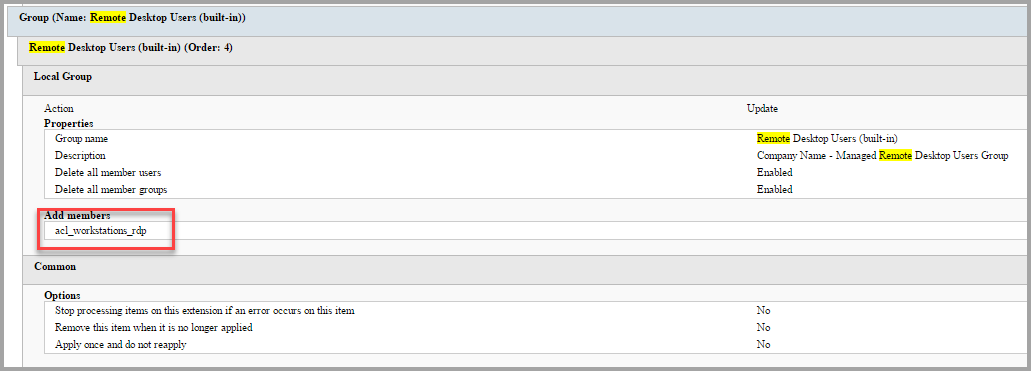
-
Backup Operators (built-in) ? This group is designed to manage the accounts that are members of this group. Most organizations do not use this group so it is a good practice to force it to be empty. No changes are required unless your company uses this group.
-
Power Users (built-in) - This group is designed to manage the accounts that are members of this group. Most organizations do not use this group so it is a good practice to force it to be empty. No changes are required unless your company uses this group.
-
Offer Remote Assistance Helpers ? Modify this group and change the place holder group with the Domain Local group created earlier in this paper. If your company does not use Remote Assistance, remove the GPO entry.
NOTE: THE BEST PRACTICE IS TO ADD STANDARD DOMAIN USER ACCOUNTS TO ALLOW RDP ACCESS AND THEN FORCE THEM TO PERFORM A RUN AS TO PERFORM ADMINISTRATIVE TASKS. SINCE THE LOGON CACHE IS SET TO 0, THIS HELPS MITIGATE THE RISK OF LEAVING ADMINISTRATIVE CACHED CREDENTIALS ON THE CLIENTS.